It may be spring, but it’s not too soon to look ahead to summer weather, especially when El Niño – a player in last year’s especially brutal summer – is rapidly weakening and will all but vanish by the time the season kicks into gear.
El Niño’s disappearing act doesn’t mean relief from the heat. Not when the world is heating up due to human-driven climate change. In fact, forecasters think it could mean the opposite.
What this summer’s weather could look like
El Niño is a natural climate pattern marked by warmer than average ocean temperatures in the equatorial Pacific. When the water gets cooler than average, it’s a La Niña. Either phase can have an effect on weather around the globe.
By June, forecasters expect those ocean temperatures to hover close to normal, marking a so-called neutral phase, before La Niña builds in early summer, according to NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center.
But the strength of El Niño or La Niña’s influence on US weather isn’t uniform and varies greatly based on the strength of the phenomena and the season itself.
The influence of El Niño or La Niña on US weather isn’t as clear-cut in the summer as it is in the winter, especially during a transition between the two phases, said Michelle L’Heureux, a climate scientist with the Climate Prediction Center.
Temperature differences between the tropics and North America are more extreme in the winter, L’Heureux explained. This allows the jet stream to become quite strong and influential, reliably sending storms into certain parts of the US.
In the summer, the difference in temperature between the two regions isn’t as significant and the obvious influence on US weather wanes.
But we can look back at what happened during similar summers to get a glimpse of what could come this summer.
In short: It’s not cool.
The summer of 2016 was one of the hottest on record for the Lower 48. La Niña conditions were in place by midsummer and followed a very strong El Niño winter.
Summer 2020 followed a similar script: La Niña conditions formed midsummer after a weak El Niño winter but still produced one of the hottest summers on record and the most active hurricane season on record.
Then there’s the fact that these climate phenomena are playing out in a warming world, raising the ceiling on the extreme heat potential.
“This obviously isn’t our grandmother’s transition out of El Niño – we’re in a much warmer world so the impacts will be different,” L’Heureux, said. “We’re seeing the consequences of climate change.”
Current summer temperature outlooks for the US are certainly bringing the heat.
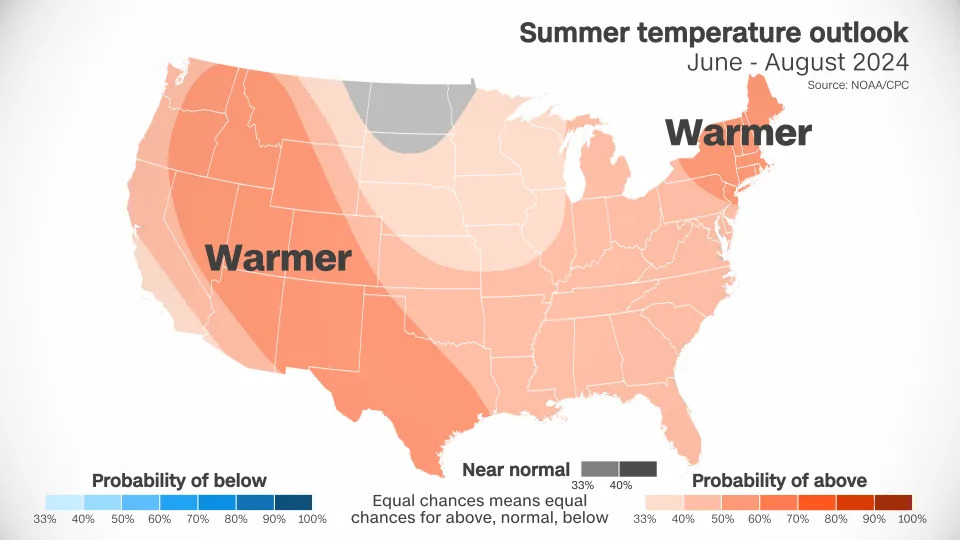
Above-average temperatures are forecast over nearly every square mile of the Lower 48. Only portions of the Dakotas, Minnesota and Montana have an equal chance of encountering near normal, above- or below-normal temperatures.
A huge portion of the West is likely to have warmer conditions than normal. This forecast tracks with decades of climate trends, according to L’Heureux.
Summers have warmed more in the West than in any other region of the US since the early 1990s, according to data from NOAA. Phoenix is a prime example. The city’s average July temperature last year was an unheard-of 102.7 degrees, making it the hottest month on record for any US city. It was also the deadliest year on record for heat in Maricopa County, where Phoenix is located.
Forecasts also show a worrying precipitation trend for parts of the West.
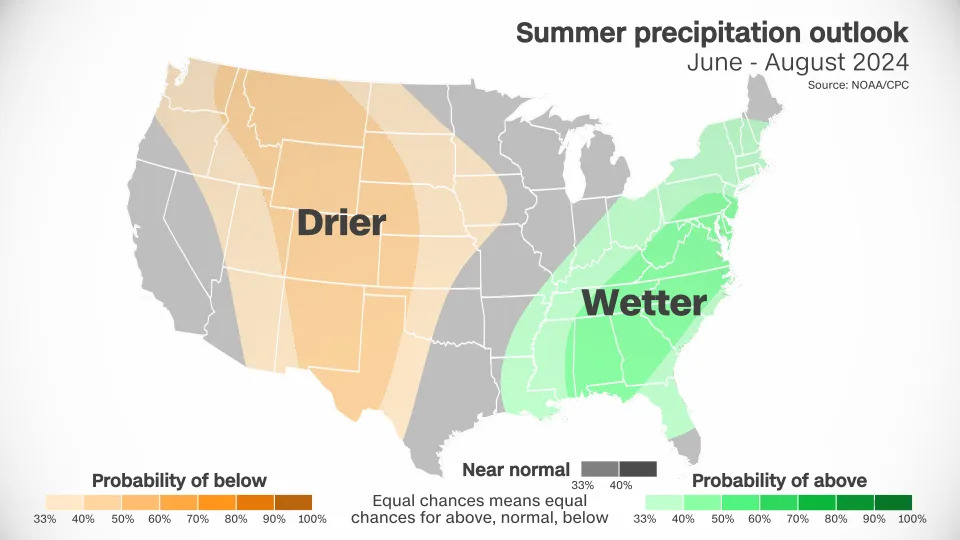
Large sections of the West and the central US are likely to be drier than normal. This dryness, combined with above-normal heat, which only amplifies the dryness, could be a recipe for new or worsening drought.
Wetter than normal conditions are in the forecast from the Gulf Coast to the Northeast. Stormy weather could be a consistent companion for much of the East – but whether it comes from typical rain and thunderstorms or tropical activity won’t be known for months.
A brutal summer also predicted in the water
Heat isn’t the only threat to look out for.
The strengthening La Niña conditions, coupled with ocean temperatures which have been at record highs for over a year, could supercharge the Atlantic hurricane season.
A warming world generates more fuel for more tropical activity and stronger storms. La Niña tends to produce favorable atmospheric conditions to allow storms to form and hold together in the Atlantic.
Early this month, forecasters at Colorado State University released their most active initial forecast ever.
“We anticipate a well above-average probability for major hurricanes making landfall along the continental United States coastline and in the Caribbean,” the group said in a news release.
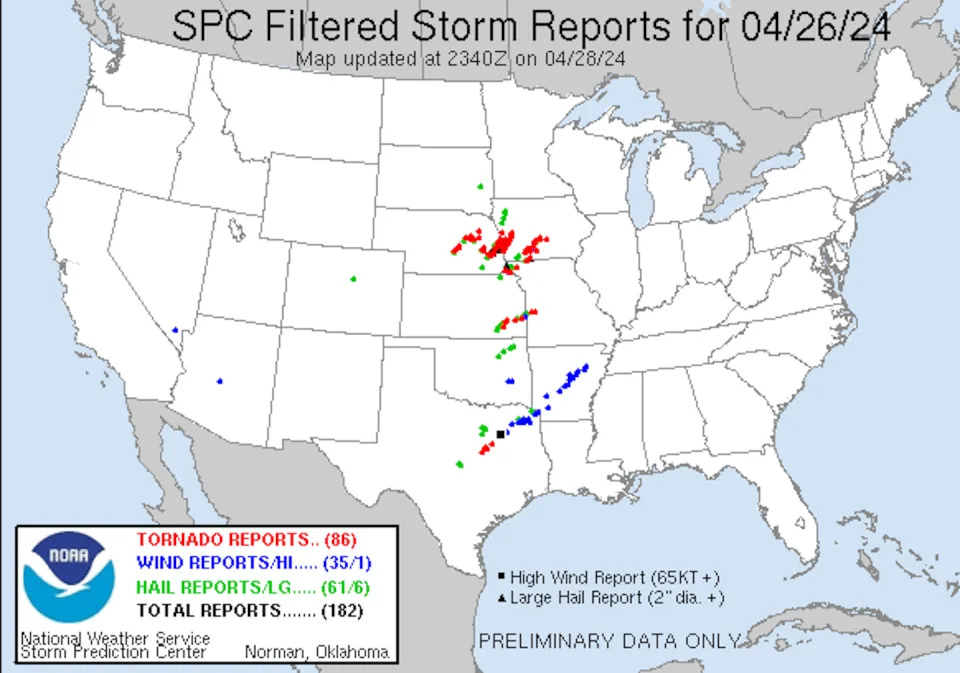
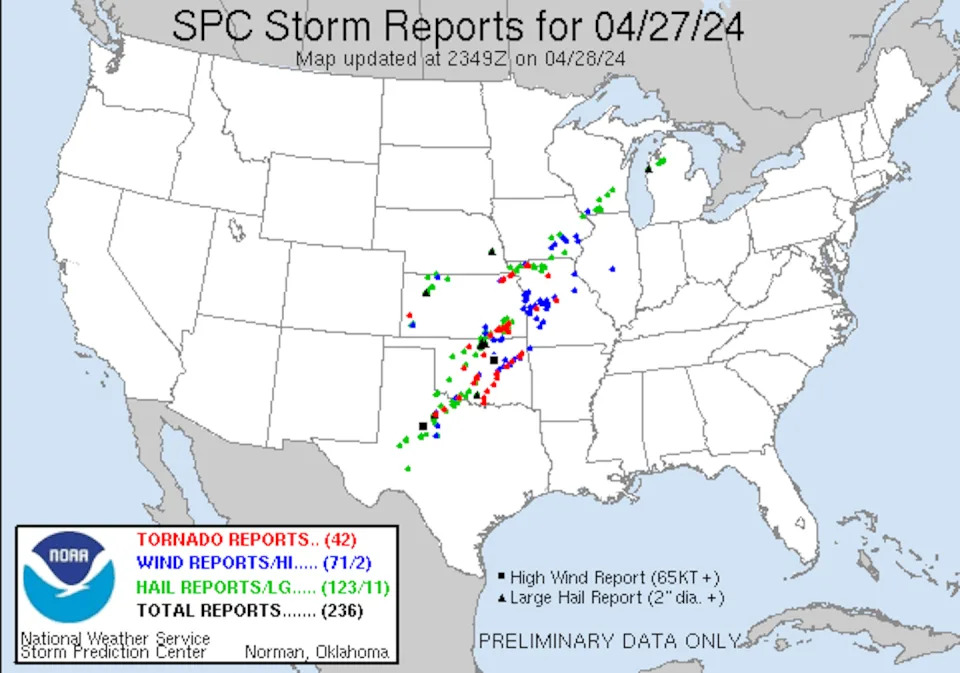
Dozens of tornadoes hit the central U.S. April 26-28, 2024, tearing through suburbs and small towns and damaging hundreds of homes from Oklahoma to Nebraska and Iowa.
Spring is tornado season in the U.S., but the tornadoes in Nebraska and Iowa were quite a bit farther north and east of what would be typical for tornadoes in late April, when tornado activity is more common in Oklahoma and Texas.
The outbreak did fit another pattern for severe weather events, however, that occur as the atmosphere transitions out of El Niño. And this is exactly what was happening in late April.
I study tornadoes and the conditions under which they form. Here’s how these storm systems develop and what El Niño has to do with it.
The right conditions for a tornado
Two basic conditions are required to produce the rotating supercell thunderstorms that are capable of generating tornadoes:
Warm moist surface conditions and cold air above.
Winds that change in both speed and direction as you move up in the atmosphere, known as vertical wind shear.
As with many severe weather outbreaks that occur in the U.S., the atmosphere became primed for storms as warm moist air at the surface was being transported northward from the Gulf of Mexico by a series of surface low-pressure systems.
Higher up, about halfway between the ground and where airplanes fly, atmospheric waves within and below the jet stream were transporting cold air through the middle part of the atmosphere. These waves, formally called Rossby waves and commonly referred to as troughs and ridges, also enhanced vertical wind shear.
A small atmospheric wave that moved through the Central Plains and Midwest on April 26, helped trigger the tornadoes in Nebraska and Iowa, including a large, destructive tornado in the suburbs of Omaha, Nebraska, and in the town of Minden, Iowa, about 30 miles away.
The following day, a bigger wave moved through Oklahoma, where tornadoes damaged several small towns that evening.
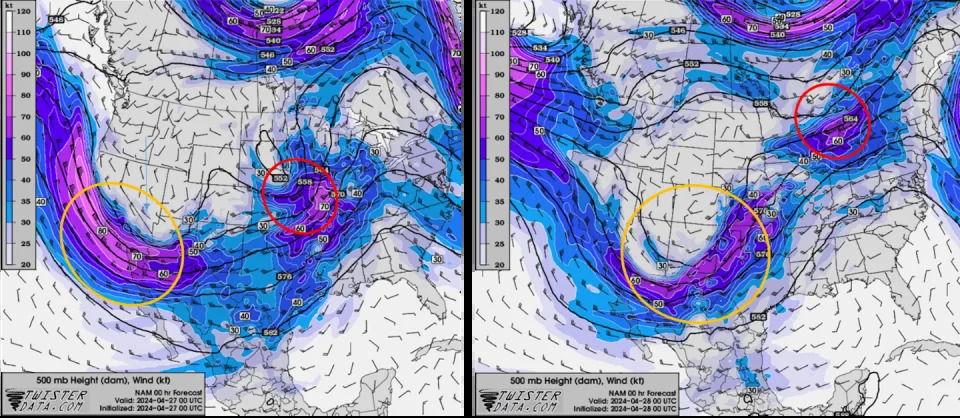
The two images show the short-wave trough, circled in red, and the longer wave, circled in orange, traveling behind it. On the left is April 26, with the short-wave trough moving through Nebraska. On the right, the longer wave is affecting Oklahoma and Kansas on April 27. TwisterData.com What was especially important was how close these parameters were to the center of the surface low-pressure system and a warm front that extended just to the east of it. The tornado-producing storms were able to tap into that instability and draw on the strong vertical wind shear generated in the vicinity of the warm front.
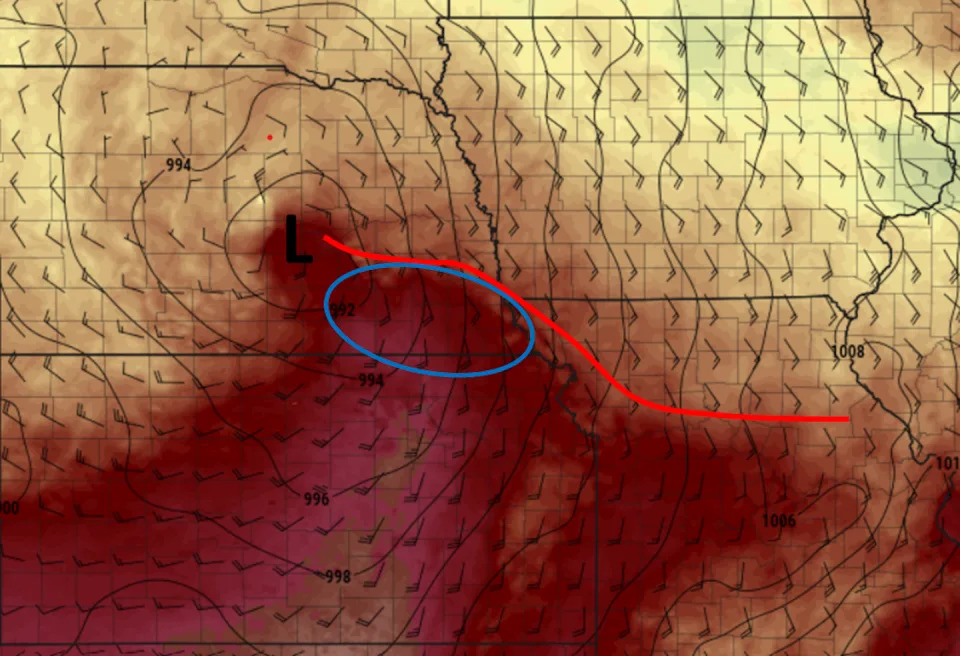
Surface temperatures (colors), winds (barbs indicating direction the wind was blowing from), surface pressure (solid black contours) indicating the location of the low pressure system (L), the warm front (red line) and the region of favorable conditions (blue circle) on the evening of April, 26, 2024. Pivotal Weather In addition to the tornadoes, the warm moist storms brought heavy rain, flash flooding and large hail across parts of the central U.S.
Picture a kid who has a helium balloon at a party and releases it – the balloon floats upward. Like that helium balloon, the warm moist air is less dense than the surrounding colder air, so it rises, accelerating upward. This upward motion releases heat, moisture and energy, and causes thunderstorms to develop.
What El Niño has to do with tornado weather
In late 2023 and early 2024, much of the world experienced above-average temperatures, likely linked to global climate change and exacerbated by El Niño. El Niño is a naturally occurring cyclical climate phenomenon that affects both the oceans and the atmosphere.
When El Niño decays, the atmospheric waves change and can become wavier, so they have a greater amplitude. That tends to enhance conditions needed for tornadoes.
The U.S. often sees more frequent tornadoes when the climate is transitioning out of El Niño. The strong El Niño of 2023-24 was decaying in April 2024, and forecasters expect it to be gone by summer.
Forecasts can save lives
The tornadoes caused severe damage in several communities as they tore apart homes and buildings. At least five people died in the storms. But early communications that warned the public of the threat for severe weather days before the storms likely saved more lives
Weather experts are getting better at predicting tornado conditions. It is not uncommon now to know days in advance of the actual event that an elevated threat exists. Forecasters have high-resolution weather models that can anticipate storms at an appropriate spatial scale to provide a sense of the likely organization of the storms and come close to the location.
The better we understand these storms’ attributes, the better those forecasts and warnings can become.
This article is republished from The Conversation, a nonprofit, independent news organization bringing you facts and trustworthy analysis to help you make sense of our complex world. It was written by: Jana Lesak Houser, The Ohio State University
A brutal summer also predicted in the water
Heat isn’t the only threat to look out for.
The strengthening La Niña conditions, coupled with ocean temperatures which have been at record highs for over a year, could supercharge the Atlantic hurricane season.
A warming world generates more fuel for more tropical activity and stronger storms. La Niña tends to produce favorable atmospheric conditions to allow storms to form and hold together in the Atlantic.
Early this month, forecasters at Colorado State University released their most active initial forecast ever.
“We anticipate a well above-average probability for major hurricanes making landfall along the continental United States coastline and in the Caribbean,” the group said in a news release.
What this summer’s weather could look like
El Niño is a natural climate pattern marked by warmer than average ocean temperatures in the equatorial Pacific. When the water gets cooler than average, it’s a La Niña. Either phase can have an effect on weather around the globe.
By June, forecasters expect those ocean temperatures to hover close to normal, marking a so-called neutral phase, before La Niña builds in early summer, according to NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center.
But the strength of El Niño or La Niña’s influence on U.S. weather isn’t uniform and varies greatly based on the strength of the phenomena and the season itself.
The influence of El Niño or La Niña on U.S. weather isn’t as clear-cut in the summer as it is in the winter, especially during a transition between the two phases, said Michelle L’Heureux, a climate scientist with the Climate Prediction Center.
Temperature differences between the tropics and North America are more extreme in the winter, L’Heureux explained. This allows the jet stream to become quite strong and influential, reliably sending storms into certain parts of the U.S.
In the summer, the difference in temperature between the two regions isn’t as significant and the obvious influence on U.S. weather wanes.
But we can look back at what happened during similar summers to get a glimpse of what could come this summer.
In short: It’s not cool.
The summer of 2016 was one of the hottest on record for the Lower 48. La Niña conditions were in place by midsummer and followed a very strong El Niño winter.
Summer 2020 followed a similar script: La Niña conditions formed midsummer after a weak El Niño winter but still produced one of the hottest summers on record and the most active hurricane season on record.
Then there’s the fact that these climate phenomena are playing out in a warming world, raising the ceiling on the extreme heat potential.
“This obviously isn’t our grandmother’s transition out of El Niño – we’re in a much warmer world so the impacts will be different,” L’Heureux, said. “We’re seeing the consequences of climate change.”
Current summer temperature outlooks for the U.S. are certainly bringing the heat.
Above-average temperatures are forecast over nearly every square mile of the Lower 48. Only portions of the Dakotas, Minnesota and Montana have an equal chance of encountering near normal, above- or below-normal temperatures.
A huge portion of the West is likely to have warmer conditions than normal. This forecast tracks with decades of climate trends, according to L’Heureux.
Summers have warmed more in the West than in any other region of the U.S. since the early 1990s, according to data from NOAA. Phoenix is a prime example. The city’s average July temperature last year was an unheard-of 102.7 degrees, making it the hottest month on record for any U.S. city. It was also the deadliest year on record for heat in Maricopa County, where Phoenix is located.
Forecasts also show a worrying precipitation trend for parts of the West.
Large sections of the West and the central U.S. are likely to be drier than normal. This dryness, combined with above-normal heat, which only amplifies the dryness, could be a recipe for new or worsening drought.
Wetter than normal conditions are in the forecast from the Gulf Coast to the Northeast. Stormy weather could be a consistent companion for much of the East – but whether it comes from typical rain and thunderstorms or tropical activity won’t be known for months.